If your organization accelerated the implementation of new telehealth systems to meet the demand brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic, you may find yourself regrouping now and contemplating the need to perform a detailed risk analysis of all of your telehealth assets, policies and procedures.
The cyber risk management of highly integrated systems such as those of a telehealth environment can be a complicated and time-consuming task for healthcare organizations large and small. Combining that challenge with the responsibility of making sure these systems are risk analyzed and risk-managed in a way that meets with published expectations of HIPAA and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) is a non-trivial undertaking.
For a review of the nine essential elements outlined by OCR and exactly how these elements should be applied, please see the blog titled “Performing OCR-Quality® Risk Analysis on New Systems and Processes.”
To help any healthcare organization more effectively manage its cyber risks related to telehealth, while at the same time meeting the requirements outlined by OCR, I am going to review how Clearwater’s IRM|Analysis® software can be used to assess the security of electronic protected health information (ePHI) in four telehealth modalities:
- Mobile Health (mHealth) meaning the use of tablets, smartphones, wearables, and other mobile devices to monitor patient health and wellness.
- Live Interactive Services such as video chat, video conferencing, and live chat are some of the technologies that enable real-time interactions and allow healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat disease or provide medical advice to patients remotely.
- Store-and-Forward, which refers to a telehealth system where the provider uses recorded medical data sent from a remote location to diagnose or offer treatment in a non-real time setting.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) RPM uses a variety of telecommunication technologies to monitor patient health remotely. Often used to manage chronic and intensive-care conditions like heart disease, diabetes, asthma, for example.
Clearwater’s IRM|Analysis software is not only flexible, but it is also scalable. It is designed to address the needs of complex systems such as EMRs, entire medical device catalogs, and other Medical IoT (MIoT) devices, including telehealth systems. In this example, we are able to define systems that match each of the four telehealth modalities mentioned above in their entirety (See Figure 1).
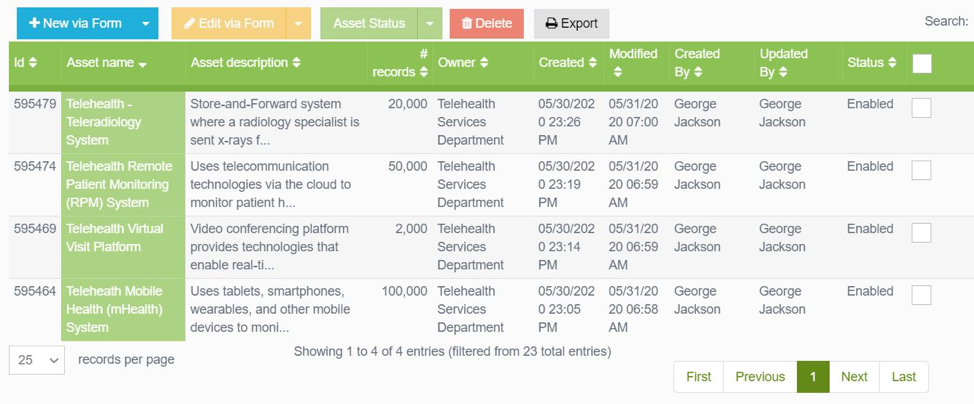 Figure 1. IRM|Analysis Four Telehealth Modalities Inventory List Illustration.
Figure 1. IRM|Analysis Four Telehealth Modalities Inventory List Illustration.
Within the asset portion of the software, an organization can provide descriptions of each system at any level of detail desired. Within the asset, module organizations can specify recovery time (RTO) and recovery point (RPO) objectives, summarize the data flow of sensitive information, specify actual or approximate numbers of sensitive records involved, and fully characterize and enumerate each critical system component type.
Once the Clearwater IRM|Analysis software is populated with telehealth asset information, risk analysts can assess present controls and evaluate threats and vulnerabilities to determine risk ratings for all assets at an extremely granular level. Secure transmission of sensitive data requires the implementation of reasonable and effective security controls at each step of the telehealth system’s operation. The built-in, continuously updated algorithms with IRM|Analysis let you know which vulnerabilities, threats, and controls are applicable to your organization’s unique telehealth systems and platforms (See Figure 2).
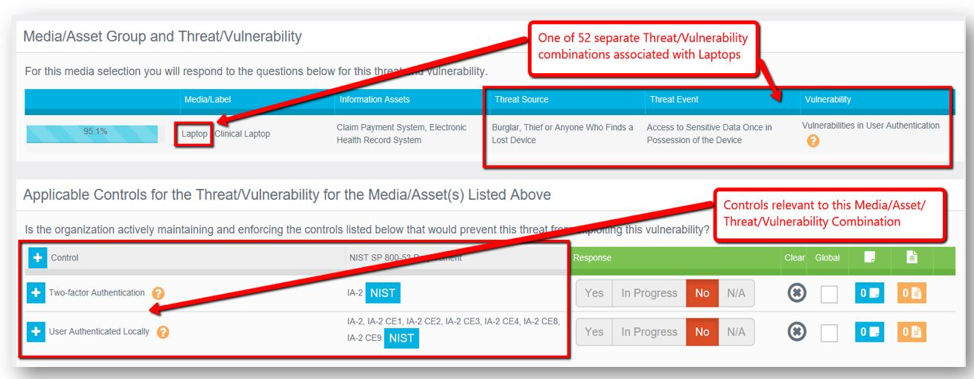 Figure 2. IRM|Analysis enables detailed and thorough analysis of current controls.
Figure 2. IRM|Analysis enables detailed and thorough analysis of current controls.
It is important to point out that these complex systems are typically transmitting patient data over internal and external networks across a variety of locations. Clearwater’s Component Expert System (CES), embedded in IRM|Analysis, enables hospitals and health systems to complete the security risk analysis process more efficiently across the enterprise by logically grouping similar information system components based on their properties and associated controls. This patented technology automatically identifies relevant cyber and information risk scenarios, thereby facilitating a more effective risk assessment process.
At the heart of every OCR-Quality® Risk Analysis is a determination of risk level for all critical components based upon the likelihood of a risk being exploited and the severity of its impact (See Figure 3).
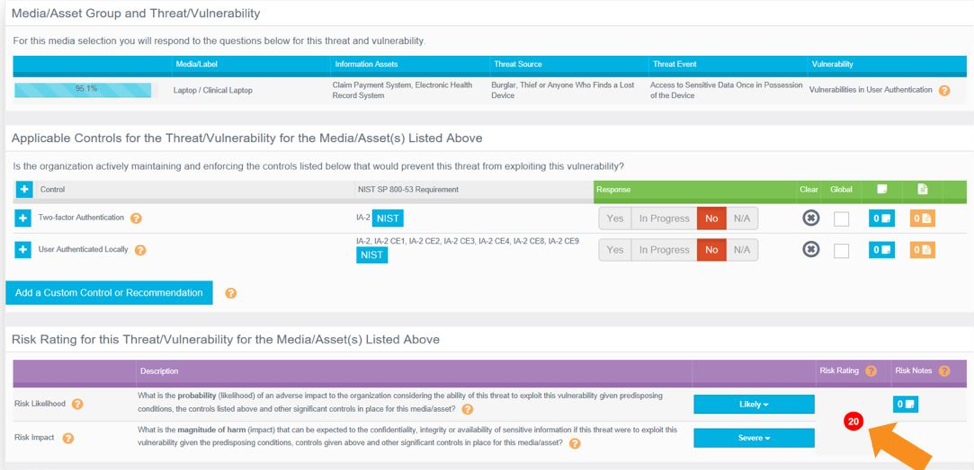 Figure 3. IRM|Analysis powers the organization’s ability to accurately determine levels of risk.
Figure 3. IRM|Analysis powers the organization’s ability to accurately determine levels of risk.
Once again, this analysis is driven by Clearwater’s proprietary algorithms that are constantly being updated in accordance with NIST and OCR guidance and enhanced through the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence. These measures provide reliable guidance and support to your risk analysts and their ongoing assessment and documentation of the risks to your telehealth environment (See Figure 4).
Reports from IRM|Analysis also can be used to further assist the organization in understanding and managing telehealth risks. Additionally, reports from IRM|Analysis can be printed and submitted to OCR and used to support your organization’s Promoting Interoperability (formerly Meaningful Use) attestation. The version history feature within the software assists organizations in demonstrating their compliance with the requirement to conduct periodic reviews and updates.
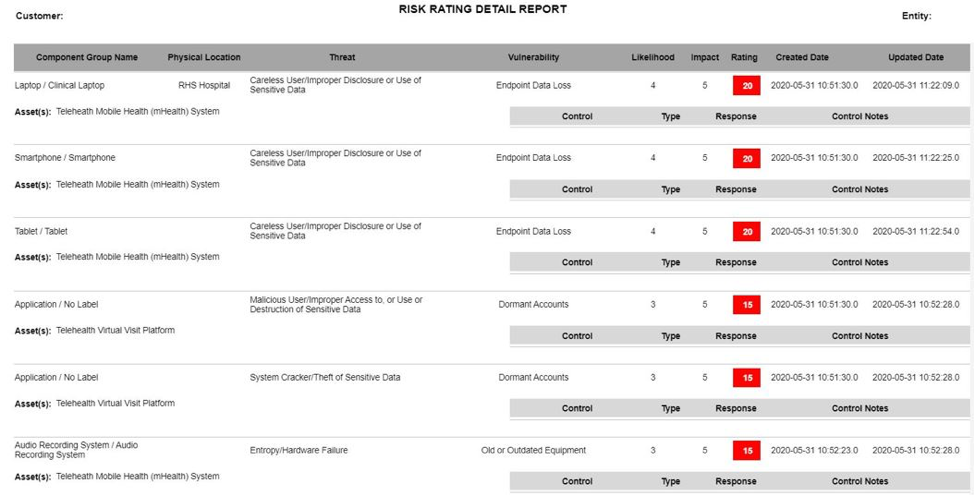 Figure 4. The Risk Rating Detail Report is just one of a variety of reports, available at the push of a button, in IRM| Analysis.
Figure 4. The Risk Rating Detail Report is just one of a variety of reports, available at the push of a button, in IRM| Analysis.
As a follow up to risk analysis, the IRM|Analysis software also helps healthcare organizations orchestrate and manage the appropriate risk response activities (See Figure 5).
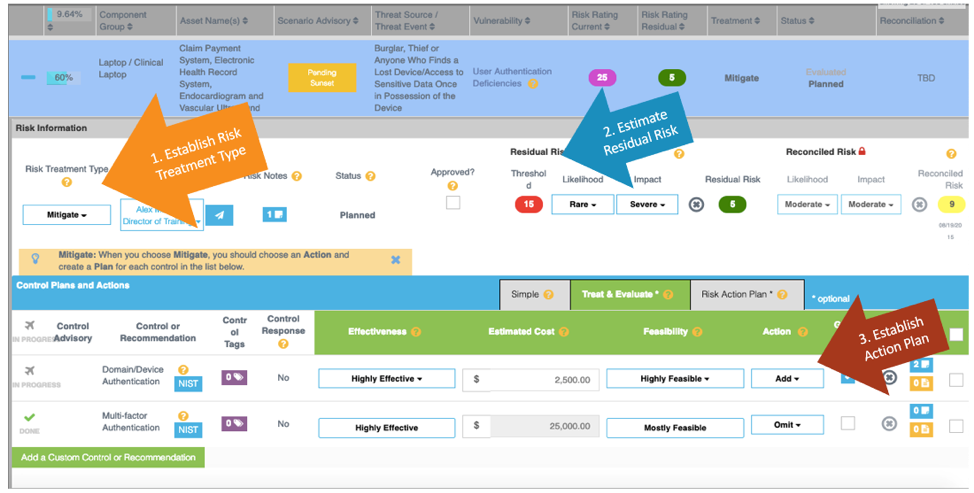 Figure 5. IRM|Analysis also supports compliance the required implementation specification at § 164.308(a)(1)(ii)(B), for Risk Management.
Figure 5. IRM|Analysis also supports compliance the required implementation specification at § 164.308(a)(1)(ii)(B), for Risk Management.
Once the Clearwater IRM|Analysis software is fully populated, it becomes an organization’s database repository for ongoing risk analysis and risk management activity. A robust platform created to meet explicit HIPAA Security Rule requirements and the OCR audit protocol pertaining to risk analysis requirements at 45 C.F.R. §164.308(a)(1)(ii)(A) and the required implementation specification at 45 C.F.R § 164.308(a)(1)(ii)(B) for Risk Management.
Taking action now to build a repository of telehealth-related risks is certain to pay dividends moving forward with some predicting that $250 billion of U.S. healthcare spend could be virtualized in the wake of COVID-19[i]. We’re not likely to see the dial turned back to where it was before the pandemic.
[i]www.mckinsey.com – Telehealth: A quarter-trillion dollar post-COVID-19 reality?



